FEATURED ARTICLES
This section includes brief descriptions of articles soon to be or recently published by the Journal of Mechanical Design. These featured articles highlight recent research developments and emerging trends in mechanical design.
For Abstracts and Full Articles please see ASME’s Digital Collection.
2026
January 27, 2026
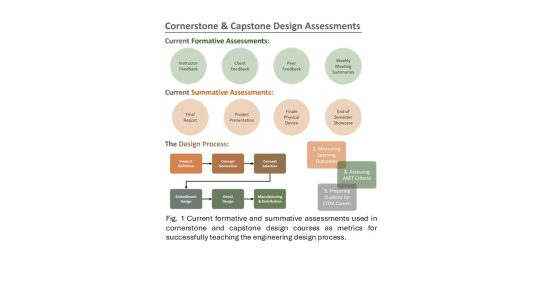
Undergraduate engineering students are expected to develop strong design and professional skills. These skills are often difficult to teach and assess effectively throughout a degree program. This article examines how design education develops from introductory courses through capstone design within undergraduate programs and highlights the need for structured and repeated formative assessment. The study synthesizes evidence from multiple institutions to capture diverse approaches to teaching and assessing engineering design. Their findings show that while programs consistently introduce hands-on teamwork and problem-solving experiences, many programs lack consistent formative feedback and structured reflection needed for real skill development. Survey data, public information, and faculty vignettes were leveraged to reveal that most programs assess design outcomes rather than the learning process itself. Multiple design projects, frequent feedback, and iterative reflection opportunities are recommended in order to reinforce what students learn about the engineering design process over time. In addition, the work calls for better integration of professional skills into undergraduate design experiences. These findings invite educators to rethink how design learning evolves, ensuring that skill development continues well beyond the classroom and prepares future engineers to meet the complex, multidisciplinary challenges of modern practice.
2025
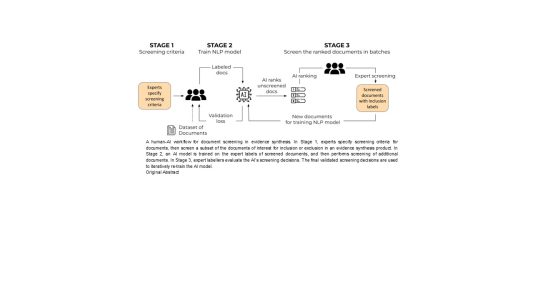
December 30, 2025
2025
February 10, 2025

Featured Articles Editor:
Anastasia Schauer
The University of Texas at Austin
Keyword Search
Search by Year
Search by Topics