Michael G. Kapteyn and Karen E. Willcox
ASME. J. Mech. Des. September 2022; 144(9): 091710. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4054907
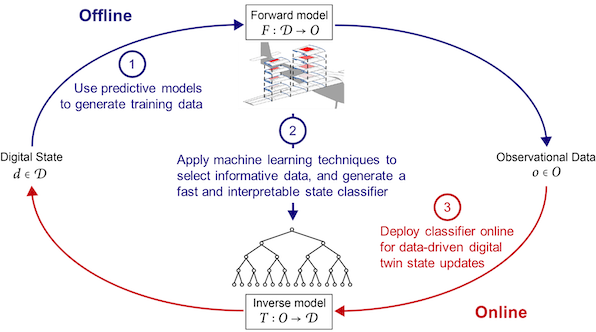
A Digital Twin is a personalized, dynamically evolving virtual model of a physical, natural or biological system. Digital Twins are characterized by a dynamic and continuous two-way flow of information between the computational models and the physical system. Digital Twins have emerged as a promising paradigm for monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing complex engineering systems. A core component of a Digital Twin is a computational model that ingests data from sensors, inspections, or other diagnostic systems in order to adapt over time to persistently represent the state of the system. It is often challenging to determine which data should be collected and how this data should be processed, in order to most accurately and efficiently update the Digital Twin. This work develops a methodology for combining predictive physics-based models with an interpretable machine learning technique in order to determine optimal sensor placement and dynamic sensor scheduling decisions for Digital Twins. The proposed approach is demonstrated for the task of selecting structural health sensing strategies for a Digital Twin of an unmanned aerial vehicle.